Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) is a type of dialysis that is used as a treatment option for individuals with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or kidney failure. It is a form of peritoneal dialysis that offers flexibility and convenience for patients who require regular dialysis.
CAPD utilizes the peritoneal membrane, a lining inside the abdomen, as a natural filter to remove waste products and excess fluid from the body. Unlike hemodialysis, which is performed in a dialysis center using a machine, CAPD allows patients to perform dialysis at home or in any clean environment without the need for a machine.
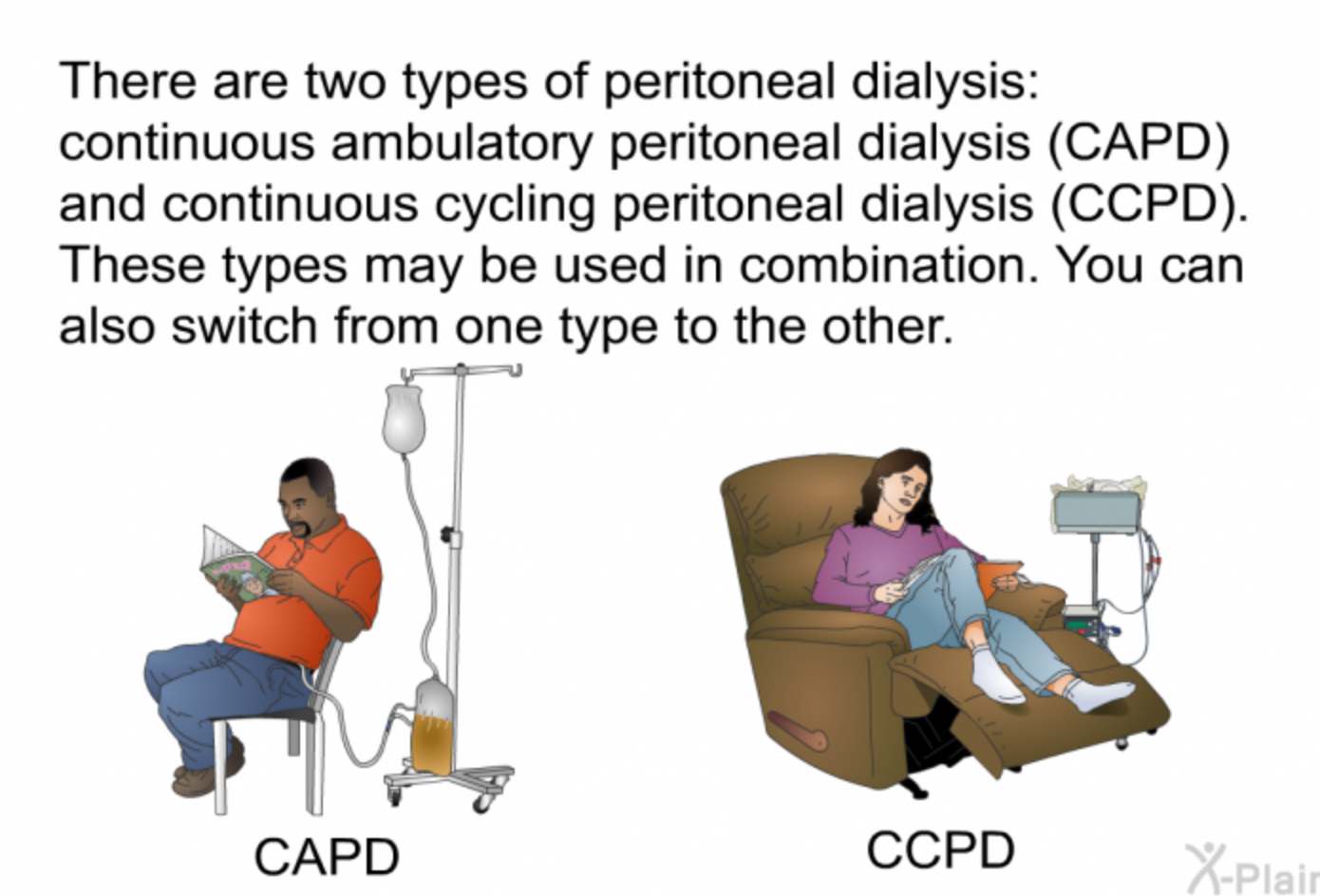
The CAPD procedure involves the insertion of a soft, flexible tube called a catheter into the abdomen through a small surgical incision. The catheter is left in place, and the peritoneal cavity is filled with a sterile dialysis solution called dialysate. The dialysate remains in the abdomen for a prescribed amount of time, known as the dwell time, during which waste products and excess fluid are drawn from the blood vessels in the peritoneal membrane into the dialysate solution. After the dwell time, the used dialysate is drained from the abdomen, and fresh dialysate is instilled to begin the next cycle.
One of the key advantages of CAPD is its continuous nature. Patients perform multiple exchanges of dialysate throughout the day, typically four to six times, allowing for a more gradual removal of waste products and maintenance of fluid balance. This continuous process helps minimize fluctuations in body chemistry and offers more flexibility in terms of scheduling compared to hemodialysis, which is typically performed three times a week in a dialysis center.
Another benefit of CAPD is its simplicity and convenience. Once trained by healthcare professionals, patients can perform the procedure independently at home. This provides greater freedom and flexibility, allowing individuals to maintain their daily routines, continue working, and engage in social activities with fewer restrictions compared to hemodialysis.
However, CAPD does require careful adherence to a sterile technique during exchanges and proper infection prevention measures. Regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare providers are essential to ensure the effectiveness of treatment and address any complications that may arise.
CAPD offers a viable treatment option for individuals with kidney failure, providing convenience, flexibility, and improved quality of life. It allows patients to actively participate in their own care and maintain a sense of independence. If you have kidney failure, consult with your healthcare provider to determine if CAPD is a suitable option for you.
There are two types of peritoneal dialysis: continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) and continuous cycling peritoneal dialysis (CCPD). These types may be used in combination. You can also switch from one type to the other.